The rapid evolution of technology has transformed the way we communicate, work, and live. In the heart of this digital revolution lies the question of connectivity: how do we transmit data, voice, and multimedia efficiently and reliably? The choice between wireless and wired connections has been a long-standing debate. This blog delves into the future of structured cabling, weighing the pros and cons of both options to help you understand the role each will play in the ever-evolving landscape of connectivity.
The Role of Structured Cabling
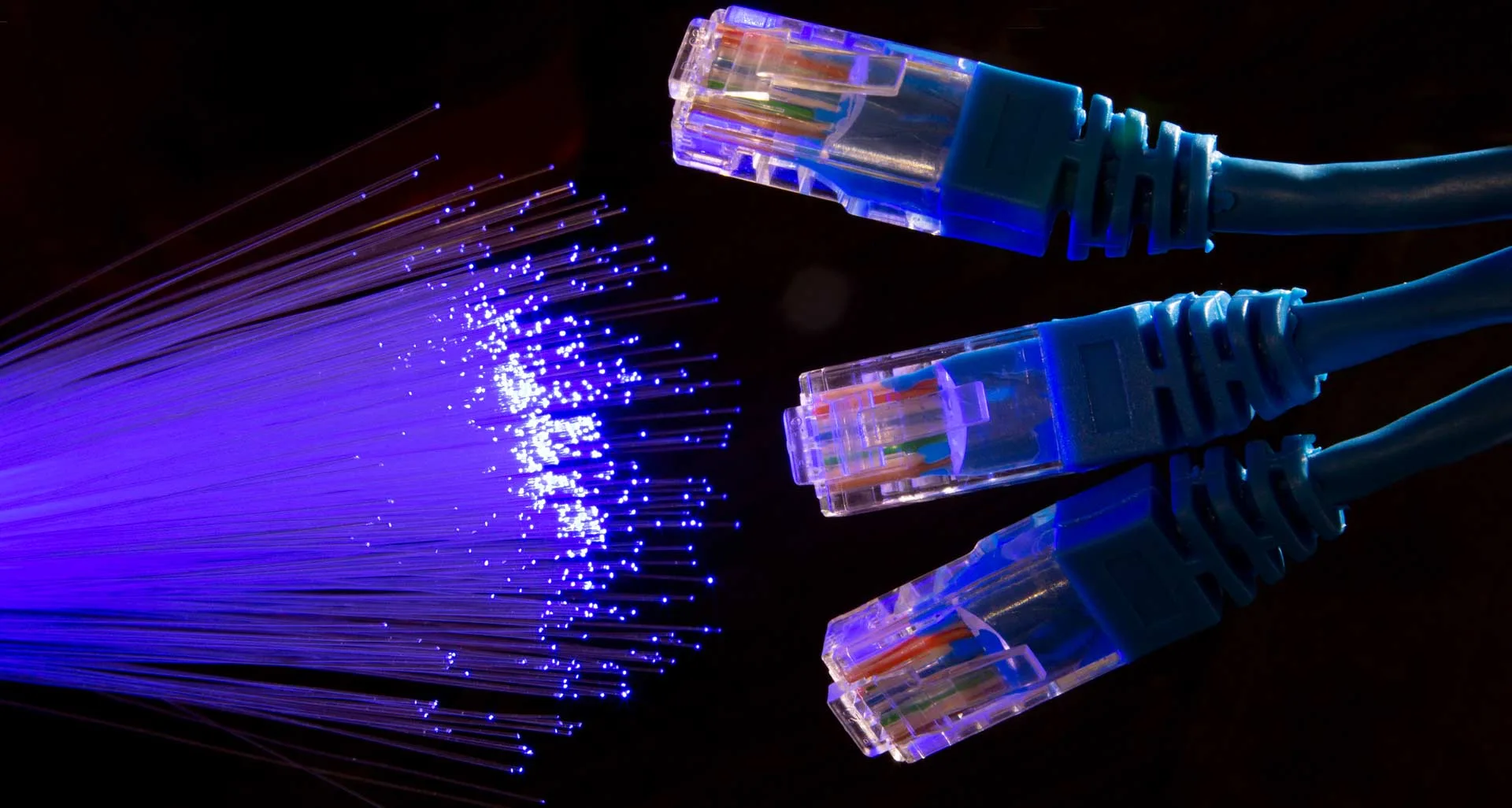
Structured cabling systems are the backbone of modern communication networks, responsible for connecting devices, servers, and switches in data centers, offices, and homes. Structured cabling not only supports data and voice but also enables power-over-ethernet (PoE) for devices like IP cameras, access points, and IoT sensors. Let’s compare the two major contenders in this arena.
Wired Connectivity: The Reliable Workhorse
Speed and Reliability: Wired connections, such as Ethernet cables, provide consistent and high-speed data transmission. They are highly reliable, with minimal interference, making them the preferred choice for critical applications like data centers and industrial settings.
Security: Wired connections are inherently more secure since they are less susceptible to interception or hacking. This makes them the ideal choice for sensitive information transfer.
Bandwidth: With the development of Cat6 and Cat6a cables, wired connections can offer bandwidths that can handle the increasing demands of modern applications, including 4K video streaming and virtual reality.
IoT and PoE: Wired connections are essential for Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) devices and the growing Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, which rely on structured cabling for both power and data transfer.
Wireless Connectivity: The Freedom of Mobility
Flexibility: Wireless connections offer the freedom to move around without being tethered to a cable. This makes them ideal for mobile devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Scalability: Wireless networks are easier to expand and reconfigure. Businesses and homes can adapt their network setups more quickly to meet changing needs.
Cost and Installation: Setting up a wireless network can be cost-effective, especially in existing buildings where wiring may be challenging. The absence of physical cables reduces installation costs.
Convenience: Wireless is convenient for home users who want to connect their devices without the hassle of running cables throughout their space.
The Future of Structured Cabling: It’s evident that both wired and wireless connections have their advantages and disadvantages. The future of structured cabling will likely involve a hybrid approach that leverages the strengths of both technologies to create more efficient and reliable networks.
Wi-Fi 6 and Beyond: The development of Wi-Fi 6 and upcoming Wi-Fi standards promise faster wireless speeds and improved performance. These advancements will make wireless networks even more compelling for various applications.
5G and Edge Computing: The rollout of 5G networks and the adoption of edge computing will redefine wireless connectivity. These technologies will enable faster, low-latency connections, making wireless a viable option for even more applications.
Fiber Optics: Fiber optics, which form the backbone of wired connectivity, will continue to evolve. The use of single-mode and multi-mode fibers will enable high-speed, long-distance data transmission, maintaining the importance of structured cabling in core network infrastructure.
Integration: The future will see a growing integration of wired and wireless technologies, with a focus on seamless handovers between them, ensuring connectivity wherever you go.
Conclusion
When it comes to ensuring the efficiency and reliability of your structured cabling solutions, choosing the right provider is paramount. Netscale Technology stands out as the preferred choice for structured cabling solution in Dubai. With a proven track record of excellence in the industry, Netscale Technology offers cutting-edge expertise, innovative solutions, and a commitment to meeting your specific connectivity requirements.Whether you’re looking to build a wired network for mission-critical applications or seeking the latest in wireless connectivity, Netscale Technology combines experience and innovation to provide tailored, future-proof cabling solutions in Dubai that empower your digital infrastructure. Choose Netscale Technology for structured cabling that is robust, scalable, and built to meet the demands of the ever-evolving world of connectivity.


rybelsus discount
[…] rybelsus tablets […]
where can i buy clomid over the counter
[…] how much does clomid cost […]